[99클럽 코테 스터디 12일차 TIL] BFS를 사용해 Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree 문제 풀이
문제
Leetcode - Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree 문제를 보고 풀이한 내용이다.
Given the root of a perfect binary tree, reverse the node values at each odd level of the tree.
- For example, suppose the node values at level 3 are
[2,1,3,4,7,11,29,18], then it should become[18,29,11,7,4,3,1,2]. Return the root of the reversed tree.
A binary tree is perfect if all parent nodes have two children and all leaves are on the same level.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
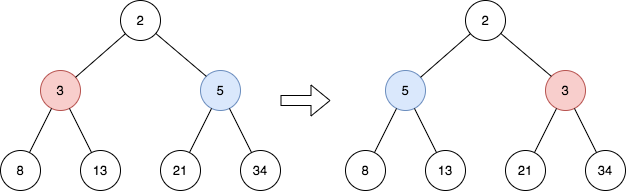
Example 1:
Input: root = [2,3,5,8,13,21,34] Output: [2,5,3,8,13,21,34] Explanation: The tree has only one odd level. The nodes at level 1 are 3, 5 respectively, which are reversed and become 5, 3.
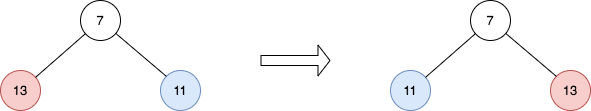
Example 2:
Input: root = [7,13,11] Output: [7,11,13] Explanation: The nodes at level 1 are 13, 11, which are reversed and become 11, 13.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,2,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2] Output: [0,2,1,0,0,0,0,2,2,2,2,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The odd levels have non-zero values. The nodes at level 1 were 1, 2, and are 2, 1 after the reversal. The nodes at level 3 were 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, and are 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 after the reversal.
풀이
완전 이진 트리의 경우, 모든 경로를 탐색한다고 했을 때는 DFS가 공간 복잡도 측면에서 O(logN)으로 더 낫다. 그러나 위 문제는 같은 레벨에 있는 노드를 탐색해 값을 바꿔주어야 한다. DFS는 한 경로를 계속해서 탐색하므로 이 문제에는 적합하지 않다고 판단해 BFS로 문제를 풀어보려 시도했다.
그러나 이번 문제는.. 너무 어려워서 Solution을 보고 코드를 이해해보기로 했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
public TreeNode reverseOddLevels(TreeNode root) {
// 루트가 null이면 입력으로 주어진 트리가 비어있으므로 그대로 반환
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
// BFS를 위한 큐 생성
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
// 루트 노드를 큐에 추가
q.offer(root);
// 현재 레벨을 나타내는 변수 초기화
int level = 0;
// 큐가 비어있지 않은 동안 반복
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// 현재 레벨의 노드 수를 저장하는 변수
int size = q.size();
// 현재 레벨의 모든 노드에 대해 반복
while (size-- > 0) {
// 큐에서 노드를 하나씩 꺼냄
TreeNode node = q.poll();
// 현재 노드의 왼쪽 자식과 오른쪽 자식이 있다면 큐에 추가
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
}
// 다음 레벨로 넘어감
level++;
// 현재 레벨이 홀수 레벨이고 큐가 비어있지 않은 경우
if (level % 2 == 1 && !q.isEmpty()) {
// 현재 레벨의 노드들의 값을 저장할 배열 생성
int[] nums = new int[q.size()];
// 배열에 현재 레벨의 노드들의 값을 저장
int i = 0;
for (TreeNode node : q) {
nums[i++] = node.val;
}
// 배열의 값을 역순으로 노드들에게 할당
int j = q.size() - 1;
for (TreeNode node : q) {
node.val = nums[j--];
}
}
}
// 모든 레벨의 처리가 끝나면 입력으로 주어진 트리를 반환
return root;
}
그런데 셀프 세션 때 발표하신 분이 DFS를 이용해서 푸신 걸 봤는데, 코드가 엄청 간결하고 직관적이었다. 이런 느낌?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public TreeNode reverseOddLevels(TreeNode root) {
sol(root.left,root.right,1);
return root;
}
public void sol(TreeNode left,TreeNode right,int l){
if(left==null || right==null) return;
if(l%2==1){
int temp=left.val;
left.val=right.val;
right.val=temp;
}
sol(left.left,right.right,l+1);
sol(left.right,right.left,l+1);
}
내가 BFS로 풀려고 고민했던 시간과 무색하게….. 넘나 예쁘고 이해가 쏙쏙 되는 코드………
풀다가 너무 안풀린다 싶으면 다른 방법을 먼저 사용해보는 것도 좋겠다는 생각이 들었다.