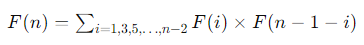[99클럽 코테 스터디 15일차 TIL] 동적 계획법으로 All Possible Full Binary Trees 풀이
문제
Leetcode - All Possible Full Binary Trees 문제를 보고 풀이한 내용이다.
Given an integer n, return a list of all possible full binary trees with n nodes. Each node of each tree in the answer must have Node.val == 0.
Each element of the answer is the root node of one possible tree. You may return the final list of trees in any order.
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has exactly 0 or 2 children.
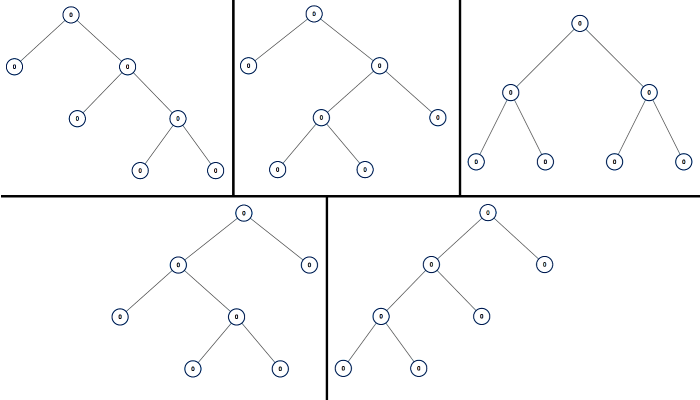
Input: n = 7
Output: [[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,null,null,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,null,null,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,null,null,0,0]]
Example 2:
Input: n = 3
Output: [[0,0,0]]
Constraints: 1 <= n <= 20
풀이
이전에 leetcode에서 풀었던 Deepest Leaves Sum 문제와 유사한 문제다.
정해진 트리 수 내에서 완전 이진 트리를 만들 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 구해야 한다. 완전 이진 트리의 특성인 “각 노드는 자식 노드가 없거나 두 개의 자식 노드를 가진다” 라는 법칙에 따라 루트 노드를 포함하면 n은 무조건 홀수여야 한다. 따라서 짝수인 경우는 빈 리스트를 반환해야 한다.
재귀 호출을 이용해서 각 노드를 탐색하고, 만들어진 경로를 결과 리스트에 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class Solution {
public List<TreeNode> allPossibleFBT(int n) {
List<TreeNode> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (n % 2 == 0) {
return result; // n이 짝수이면 빈 리스트 반환
}
if (n == 1) {
result.add(new TreeNode(0));
return result;
}
for (int leftNodes = 1; leftNodes < n; leftNodes += 2) {
int rightNodes = n - 1 - leftNodes;
List<TreeNode> leftTrees = allPossibleFBT(leftNodes);
List<TreeNode> rightTrees = allPossibleFBT(rightNodes);
for (TreeNode left : leftTrees) {
for (TreeNode right : rightTrees) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
result.add(root);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
DP(Dynamic Programming; 동적 계획법)를 사용해 코드 개선
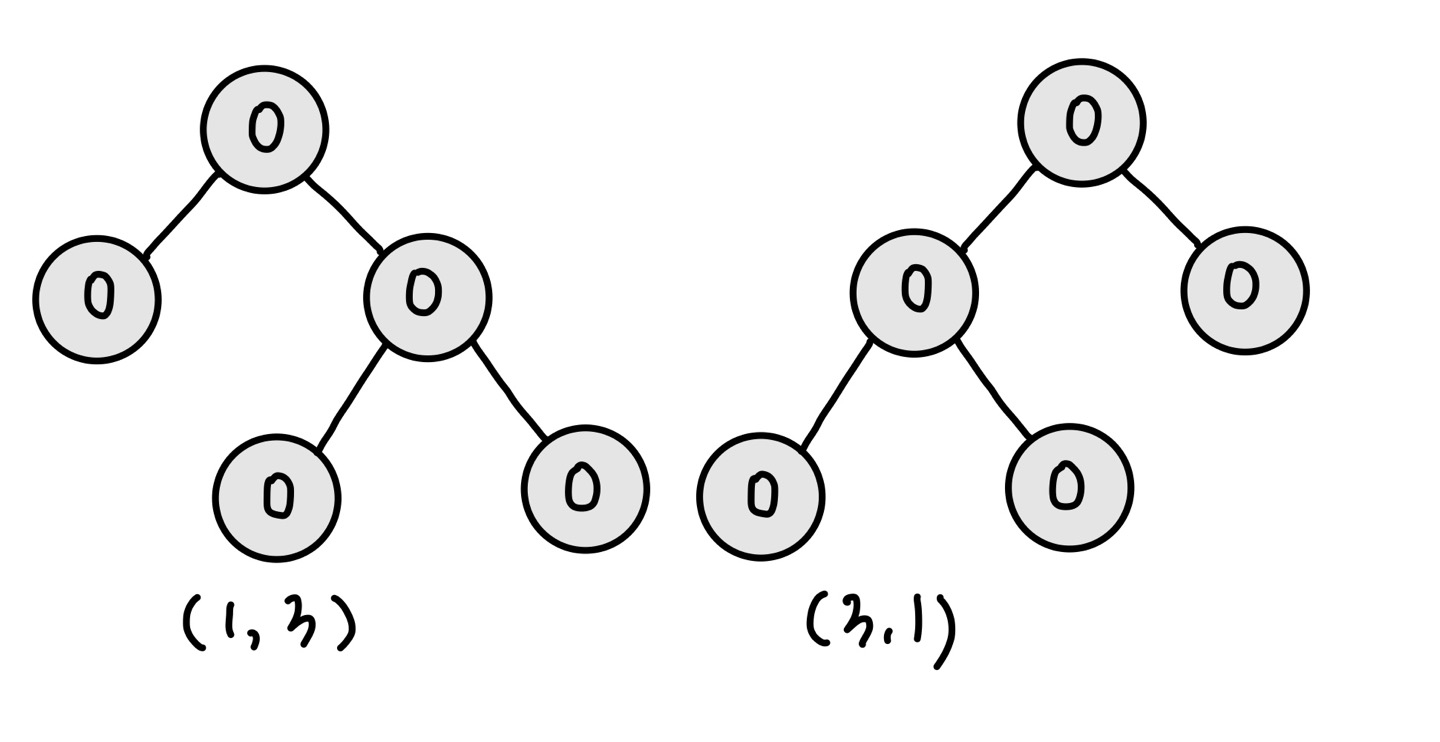
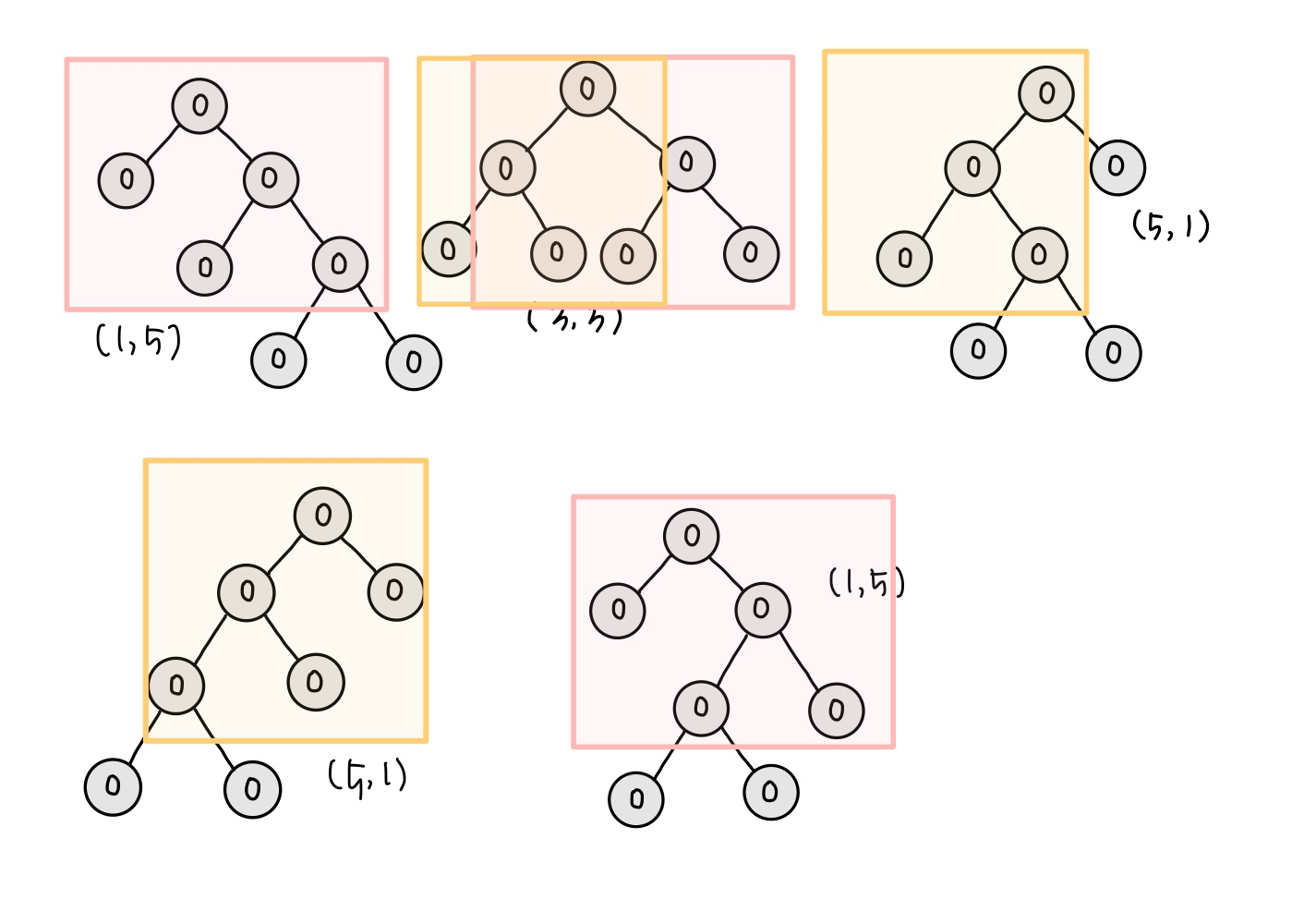
그런데 정답을 잘 살펴보면 신기한 점을 발견할 수 있다.
n이 5인 경우의 결과와 n이 7인 경우의 결과를 만들 때 동일한 부분이 존재한다. 현재의 노드를 이전의 항에 대한 식으로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
이처럼 작은 문제에서 구한 답을 큰 문제에서 그대로 사용할 수 있다면 메모이제이션을 적용할 수 있다. 메모이제이션(Memoization)이란 동일한 계산을 반복하지 않도록 중간 계산 결과를 저장하여 프로그램의 실행 시간을 단축하는 방법이다. 메모리 공간을 조금 더 사용해 연산 속도를 비약적으로 증가시킬 수 있다.
개선된 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class Solution {
// tree memorize list
private Map<Integer, List<TreeNode>> memo = new HashMap<>();
public List<TreeNode> allPossibleFBT(int n) {
if (n % 2 == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>(); // n이 짝수이면 빈 리스트 반환
}
if (n == 1) {
List<TreeNode> baseCase = new ArrayList<>();
baseCase.add(new TreeNode(0));
return baseCase;
}
if (memo.containsKey(n)) {
return memo.get(n); // 이미 계산된 경우 캐시된 결과 반환
}
List<TreeNode> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int leftNodes = 1; leftNodes < n; leftNodes += 2) {
int rightNodes = n - 1 - leftNodes;
List<TreeNode> leftTrees = allPossibleFBT(leftNodes);
List<TreeNode> rightTrees = allPossibleFBT(rightNodes);
for (TreeNode left : leftTrees) {
for (TreeNode right : rightTrees) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(0);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
result.add(root);
}
}
}
memo.put(n, result); // 결과를 캐싱
return result;
}
}