[99클럽 코테 스터디 11일차 TIL] DFS를 사용해 All Paths From Source to Target 문제 풀이
문제
Leetcode - All Paths From Source to Target 문제를 보고 풀이한 내용이다.
Given a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, find all possible paths from node 0 to node n - 1 and return them in any order.
The graph is given as follows: graph[i] is a list of all nodes you can visit from node i (i.e., there is a directed edge from node i to node graph[i][j]).
Example 1:
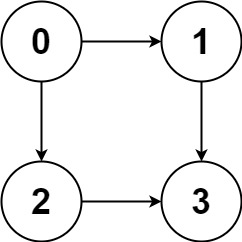
Input: graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]] Output: [[0,1,3],[0,2,3]] Explanation: There are two paths: 0 -> 1 -> 3 and 0 -> 2 -> 3.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]] Output: [[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
풀이
DFS를 사용하는 이유
이 문제는 DFS로 풀 수 있었는데, DFS로 풀이하는 이유는 다음과 같다.
DAG
주어진 그래프가 방향성 비순환 그래프(Directed Acyclic Graph; DAG)인 경우는 DFS가 효과적으로 사용된다. DAG는 순환 구조가 없으므로 DFS를 사용할 때 한 노드를 여러 번 방문하는 무한 루프에 빠질 걱정이 없다.
모든 가능한 경로 찾기
문제의 목적이 노드 0에서 노드 n - 1까지 모든 가능한 경로를 찾는 문제이다. DFS는 한 경로를 탐색하는 동안 가능한 끝 노드까지 깊이 들어가면서 경로를 형성하므로 우리가 찾고자 하는 모든 경로를 찾는 데에 적합하다.
재귀적 구조
한 노드에서 다음 노드로 이동하고, 그 다음 노드에서 또 다음 노드로 이동하는 과정을 반복하고 있으므로 재귀적으로 실행되는 DFS의 탐색 방법과 일치한다.
정답 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(graph, 0, path, result);
return result;
}
private void dfs(int[][] graph, int node, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> result) {
// 현재 노드를 경로에 추가
path.add(node);
// 만약 현재 노드가 끝 노드인 경우(목표 노드에 도달한 경우), 경로를 결과에 추가하고 종료
if (node == graph.length - 1) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
// DFS에서 돌아가기 전에 마지막 노드를 경로에서 제거
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
return;
}
// 현재 노드에서 이동할 수 있는 모든 노드에 대해 재귀적으로 DFS를 호출
for (int nextNode : graph[node]) {
dfs(graph, nextNode, path, result);
}
// DFS에서 돌아가기 전에 현재 노드를 경로에서 제거
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
각 단계에서 스택의 변화
- 초기 상태
1
2
현재 노드: 0
경로: []
- 0에서 시작하여 1로 이동
1
2
현재 노드: 1
경로: [0, 1]
- 1에서 시작하여 3으로 이동
1
2
3
현재 노드: 3
경로: [0, 1, 3]
결과에 경로 [0, 1, 3] 추가
- 1에서 시작하여 2으로 이동
1
2
현재 노드: 2
경로: [0, 1, 2]
- 2에서 시작하여 3으로 이동
1
2
3
현재 노드: 3
경로: [0, 1, 2, 3]
결과에 경로 [0, 1, 2, 3] 추가
- 0에서 시작하여 2로 이동
1
2
현재 노드: 2
경로: [0, 2]
- 2에서 시작하여 3으로 이동
1
2
3
현재 노드: 3
경로: [0, 2, 3]
결과에 경로 [0, 2, 3] 추가
따라서 모든 가능한 경로는 [[0, 1, 3], [0, 2, 3]]이 된다.